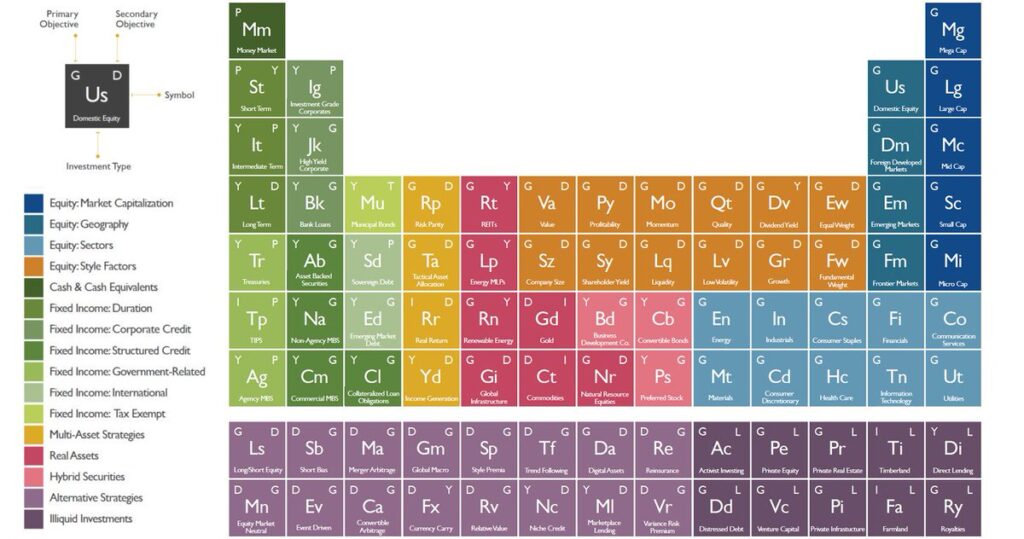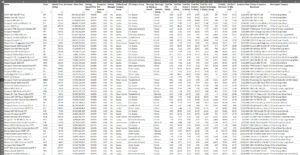
More on Investment Philosophy: The Bedrock of Advisor Guidance
An investment advisor’s philosophy is the cornerstone of their approach to managing client portfolios. It encompasses the principles, beliefs, and strategies that guide their decision-making process. This philosophy is not just a set of rules; it’s a comprehensive framework that shapes every aspect of portfolio management, from asset selection to risk assessment.
Principles and Beliefs At the heart of an investment philosophy are the core principles and beliefs that an advisor holds about the markets. These may include convictions about market efficiency, the predictability of market movements, or the importance of asset allocation. For instance, an advisor who believes in market efficiency might favor passive investment strategies, while one who sees value in market timing might adopt a more active approach.
Strategies and Approaches The strategies and approaches used by an advisor are direct reflections of their underlying philosophy. Whether it’s growth investing, value investing, or any of the myriad styles outlined above, a strategy is chosen because it aligns with the advisor’s beliefs about how to achieve the best outcomes for their clients.
Tailoring to Client Needs A key aspect of an investment philosophy is its adaptability to individual client needs. Advisors must consider each client’s risk tolerance, time horizon, and financial goals when applying their philosophy. This personalized approach ensures that the investment strategy is not only philosophically sound but also practically effective for the client’s unique situation.
Conclusion In conclusion, an advisor’s investment philosophy is a fundamental aspect of their practice. It informs every decision and interaction with clients, ensuring that their financial advice is consistent, reliable, and tailored to meet individual needs. By understanding and embracing their investment philosophy, advisors at Successful Portfolios provide clients with the confidence and clarity needed to navigate the complexities of the financial markets.